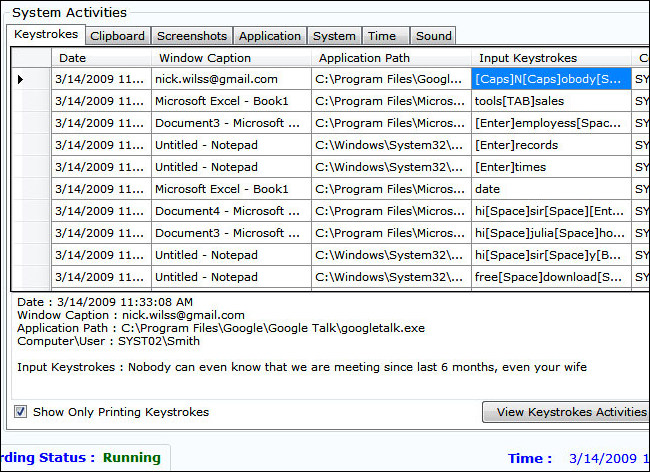
What are the Keylogger Attacks?
A Keylogger is a computer program or hardware that records every keystroke made by a computer user, especially in order to gain fraudulent access to passwords and other confidential information.
How Keyloggers Work
Keylogger attacks run hidden in the background, making a note of each keystroke you type. Software could scan through the file for certain types of text — for example, it could look for sequences of numbers that look like credit card numbers and upload them to a malicious server so they can be abused. Keylogging software may also be combined with other types of computer monitoring software, so the attacker would be able to see what you typed when you visited your bank’s website and narrow in on the information they want. A keylogger could detect the first keystrokes you typed into an online game or chat program, stealing your password. Hackers may often combine the keylogger with a screenshot program, so someone can read through a history of what you typed combined with screenshots of what was on your computer screen at the time. Related Article: 5 ways to stay safe from Bluetooth hacks and attacks. And that’s how easy it is for hackers to see and record every keystroke you press on your computer. When a hacker has an unnoticed backdoor on your computer, anything is possible, but there are a few things you can do to minimize the risk of having your keys captured:
Use antivirus software.
While there’s not a catch-all solution, and antivirus software won’t protect against sophisticated and cutting-edge keyloggers, there’s still no excuse for not using antivirus software which protects against most known keylogger software.
Use on-screen keyboards when entering passwords.
One of the limitations of most keyloggers is that they only capture actual keystrokes being pressed on the keyboard. The Windows on-screen keyboard will provide a virtual keyboard that may help circumvent keyloggers.
Use a firewall.
It’s possible lazy attackers won’t go through the effort of disguising their payloads to appear as being normal DNS (port 53) or HTTP (port 80) transmissions. A firewall might catch suspicious packets leaving your computer on port 35357.
Protect your computer against backdoors.
While all of the above is helpful when you’re already backdoored, the best thing to do is make sure you’re not exploited in the first place. This can be achieved by adding a layer of security to network monitoring. Network monitoring guarantees that any suspicious activity won’t take place unnoticed. If command and control server is gathering information the network administrator will get to know and they can take measure to stop the attack and moderate any damage. Keylogger attacks are not only threats for organizations but they are dangerous for individual machines. But with the above knowledge about how they attack and how to stay protected, you can tackle them.